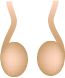The Endocrine System
The endocrine system consists of glands or parts of glands which produce hormones that are released and distributed in the human body by means of the bloodstream. The major organs of the endocrine system are the hypothalamus, the pituitary gland, the thyroid gland, the parathyroid glands, the islets of the pancreas, the adrenal glands, the testes, and the ovaries.
Humans have two systems of internal communication: the nervous system and the endocrine system. The endocrine system controls the delivery of messages through the release of chemicals known as hormones. Hormones are secreted directly into the blood by endocrine glands. Endocrine glands are found throughout the body and are responsible for releasing more than 50 hormones that control a number of essential functions in the body, including growth and development.
The Brain
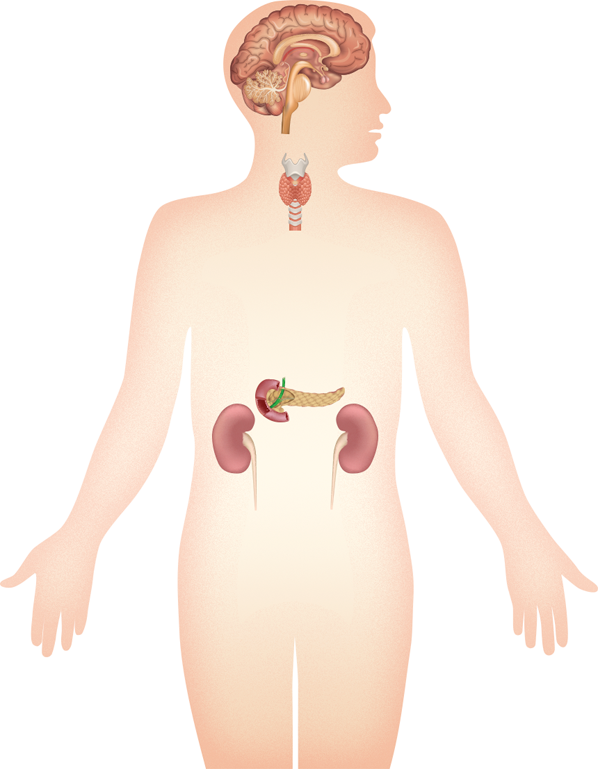
Hypothalamus
The Hypothalamus contains vital centers for controlling the automatic nervous system, body temperature and water and food intake, and is the center for primitive physical and emotional behavior.
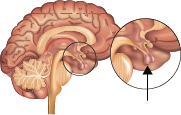
Pituitary
The pituitary gland is the master gland of the body. Compared with other endocrine glands, it produces the largest number of hormones, including some that control the other endocrine glands of the body.
Close
The Thyroid & Parathyroid
The first organ recognized as an endocrine gland was the thyroid. It consists of two bodies like small walnuts: they are connected by an isthmus beside the larynx (voice box). The parathyroids are four small glands attached to the thyroid gland, which act to maintain normal levels of calcium and phosphate in the blood and thus normal function of muscles and nerves.
Close
The Pancreas
The islets of the pancreas produce hormones necessary for the regulation of blood sugar levels - insulin and glucagons. The alpha cells of the islets secrete glucagon, which raises blood glucose (sugar) levels by stimulating the breakdown of liver glycogen. When blood sugar levels are too high, the beta cells of the pancreas secrete insulin which stimulates the uptake of glucose.
Close
Adrenal
The suprarenal or adrenal glands, each perched over one of the kidneys, are double glands. The core, or medulla, manufactures adrenalin, noradrenalin and a small amount of dopamine.
Close
The
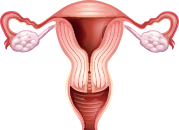
Reproductive OrgansOvaries
These double organs are the sex glands. The ovaries in females produce the egg cell (ova). They also produce sex hormones that flow through the blood and give rise to such secondary traits as the breasts of the female.
Testes
These double organs are the sex glands. The testes in males produce the germinating cells, the sperm cells. They also produce sex hormones that flow through the blood and give rise to such secondary traits as the beard of the male.
Close